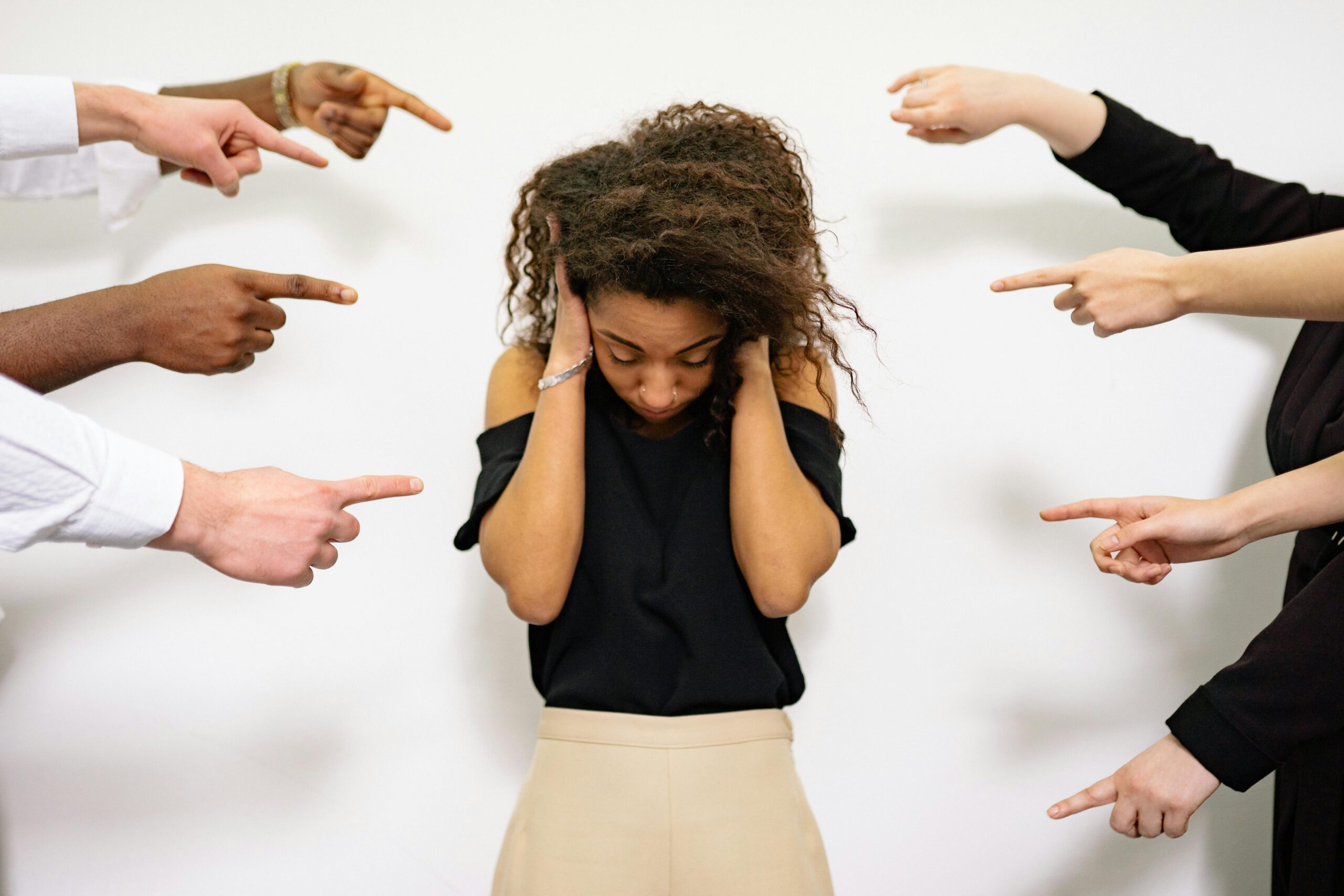
Bullying is a persistent problem that affects millions of teens worldwide, leaving lasting scars on their mental, emotional, and social well-being. The constant exposure to verbal taunts, physical aggression, or online harassment can deeply impact a young person’s self-esteem and development. Youth counseling offers a safe space and the necessary tools for teens to cope, recover, and rebuild their confidence. In this blog, we’ll explore the nature of bullying, its various forms, and its profound effects on teenagers. If you’re looking for professional help, consider exploring individual therapycounseling or psychoeducational assessments for tailored support.
For more information visit our individual counselling:
Types of Bullying
Key Causes of Family Conflicts
1. Physical Bullying:
This includes hitting, kicking, shoving, or damaging a person’s belongings. Physical bullying is the most visible form, often leaving physical and emotional scars.
Example: A teen being pushed into lockers every day at school.
2. Verbal Bullying:
Verbal bullying involves hurtful comments, name-calling, teasing, or threats. Although less visible, the emotional damage can be just as severe.
Example: A classmate constantly making demeaning comments about another’s appearance.
3. Relational Bullying (Social Exclusion):
This type focuses on damaging someone’s relationships or social standing by spreading rumors, excluding them from groups, or manipulating friendships.
Example: A teen being excluded from lunch tables or parties because of false rumors.
4. Cyberbullying:
With the rise of technology, bullying has moved online. Cyberbullying involves using social media, messaging apps, or gaming platforms to harass, intimidate, or embarrass someone.
Example: A teen receiving hurtful comments or doctored photos on Instagram.

For expert guidance on managing such situations, explore our counseling options.
How Bullying Differs from Peer Conflict
It’s essential to distinguish bullying from normal peer conflicts, which occur naturally in social interactions. Bullying is characterized by an intent to harm, a power imbalance, and repetition. In contrast, peer conflict typically involves equal parties, is unintentional, and can be resolved through communication.
Key Differences Between Bullying and Peer Conflict:
- Aspect
- Bullying
- Peer Conflict
- Power Dynamic
- Unequal; one person dominates.
- Equal; no clear power imbalance.
- Intent
- Deliberate harm.
- Usually accidental or situational.
- Repetition
- Occurs repeatedly over time.
- Typically one-time or occasional.
Recognizing these differences is crucial for parents, educators, and teens to intervene appropriately. Visit LUWGCounseling Services for actionable strategies to address these challenges.
The Impact of Bullying on Teens
Recognizing these differences is crucial for parents, educators, and teens to intervene appropriately. Visit LUWG Counseling Services for actionable strategies to address these challenges.
1. Emotional Effects
Anxiety and Depression: Teens who are bullied often experience heightened anxiety and feelings of worthlessness, leading to long-term depression if not addressed.
Low Self-Esteem: Constant negative feedback from bullies can damage a teen’s confidence and sense of self-worth.
Fear and Helplessness: The repetitive nature of bullying creates an environment where teens feel trapped and unable to escape.
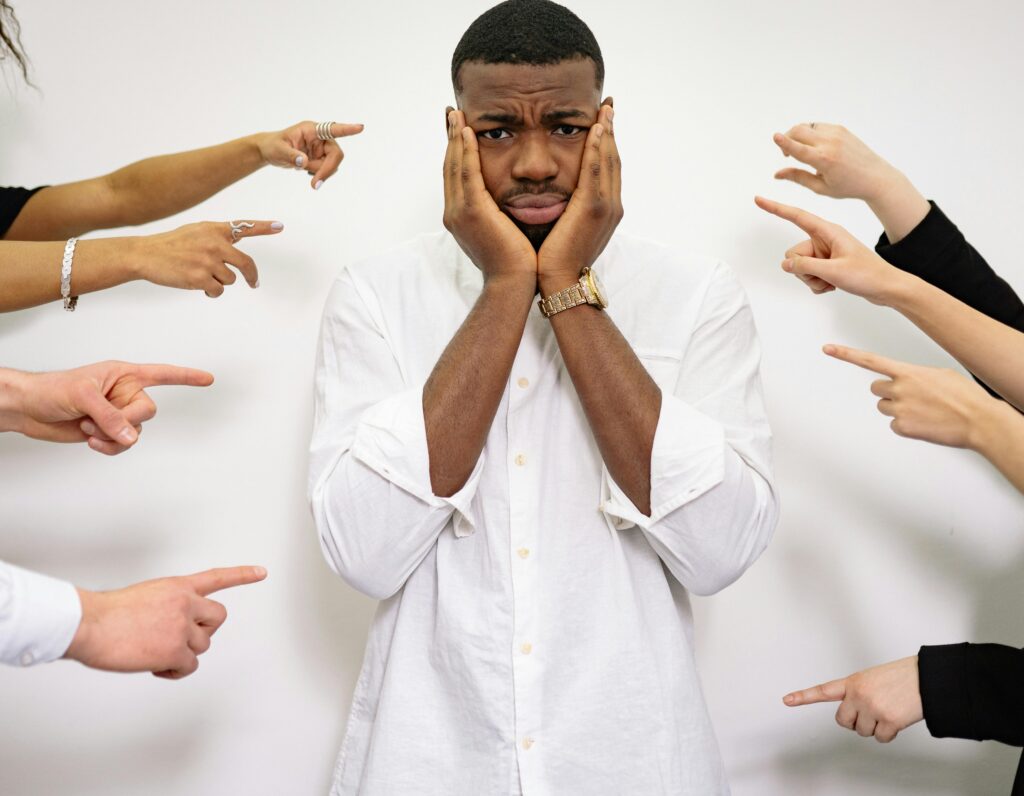


2. Social Effects
Isolation: Many victims of bullying withdraw from social activities, leading to loneliness and difficulty forming healthy relationships.
Trust Issues: Teens may find it challenging to trust others, fearing betrayal or further harm.
3. Academic Effects
Declining Performance: Bullying often distracts teens from their studies, causing grades to drop.
School Avoidance: Many teens skip school or consider dropping out entirely to avoid their bullies.
To address these challenges, schedule an individual therapy session with our experts.
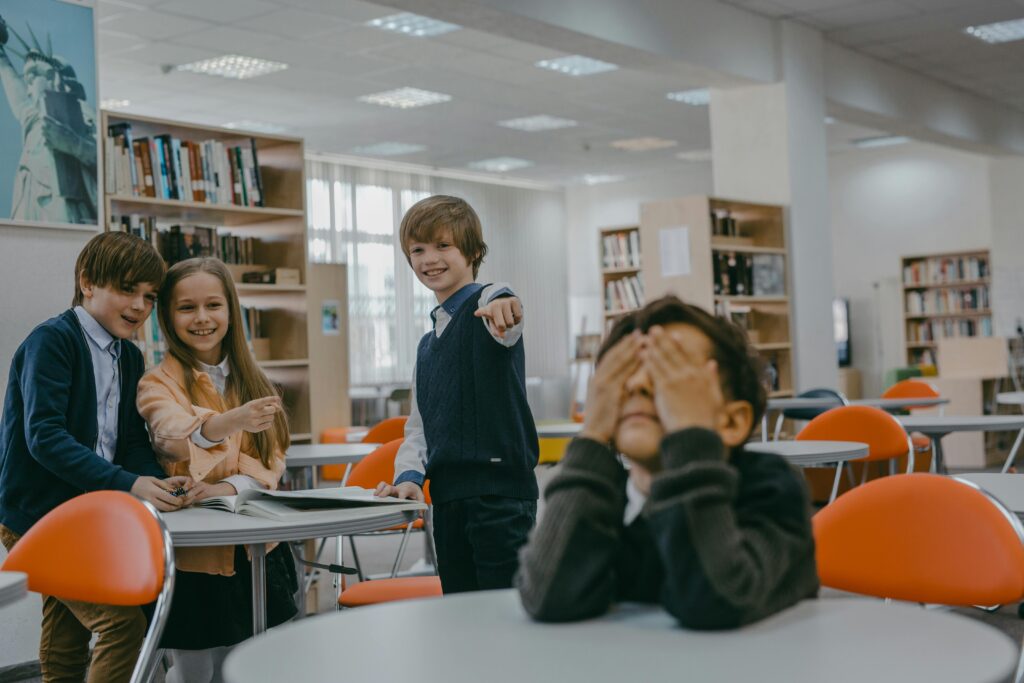


4. Physical Effects
Chronic Stress: The emotional toll of bullying can manifest physically through headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue.
Sleep Disturbances: Anxiety and fear can lead to insomnia or nightmares, further impacting health and well-being.
How Youth Counseling Helps Teens Cope
Youth counseling is an essential tool for helping teens navigate the emotional and psychological challenges posed by bullying. It provides a supportive environment where teens can process their experiences, learn coping mechanisms, and rebuild their confidence.
Key Benefits of Youth Counseling
Emotional Processing: Counseling allows teens to express their emotions freely and gain insights into how bullying has affected them.
Coping Skills Development: Teens learn practical techniques to manage stress, anxiety, and negative emotions triggered by bullying.
Self-Esteem Building: Counselors work with teens to rebuild their confidence and self-worth.
Social Support: Group therapy enables teens to connect with peers who share similar experiences, reducing feelings of isolation.
Explore our full range of counseling services for comprehensive support.

Approaches Used in Youth Counseling
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT helps teens identify negative thought patterns and replace them with positive ones. For example, a teen who internalizes bullying as their fault learns to understand it as the bully’s behavior, not their own failing. - Group Therapy:
In group therapy sessions, teens share their experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges. This sense of community can foster empowerment and reduce loneliness. - Mindfulness Training:
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, help teens manage stress and focus on the present moment rather than dwelling on negative experiences. - Role-Playing Exercises:
Role-playing allows teens to practice assertiveness, conflict resolution, and safe ways to respond to bullying scenarios, equipping them for real-life situations.
Learn more about these approaches by visiting LUWG Counseling Services.
Recognizing When Counseling is Needed
Approaches Used in Youth Counseling
Parents and caregivers should consider counseling when bullying begins to severely affect a teen’s daily life. Warning signs include:
- Persistent sadness or anxiety.
- Changes in sleeping or eating patterns.
- Avoidance of school or social events.
- Expressions of hopelessness or self-harm.
- Seeking professional help early can prevent long-term consequences.
Start by exploring our psychoeducational assessments for a deeper understanding of your teen’s needs.
Conclusion
Bullying is more than just a phase—it’s a serious issue with far-reaching effects on teens’ emotional, social, and physical health. Recognizing the signs and understanding its impact are the first steps toward helping teens heal. Youth counseling provides the support, tools, and strategies they need to regain control of their lives and build a brighter future.
In Part 2, we’ll explore practical strategies teens can use to handle bullying, how parents and caregivers can support them, and ways to create bully-free environments.