What is Andropause?
Andropause—often referred to as “male menopause”—is a condition that affects men as they age, characterized by a gradual decline in testosterone levels and other hormonal changes. Unlike menopause in women, which occurs within a defined time frame, andropause tends to develop slowly over several years. It can significantly impact physical health, emotional wellbeing, and sexual function.
Despite affecting a large percentage of the male population, andropause is still widely misunderstood or dismissed as a normal part of aging. Raising awareness is essential for identifying symptoms early and seeking effective treatment options. This article will explore the symptoms, causes, stages, treatment options, and frequently asked questions around andropause.
Key Symptoms of Andropause
- Low energy or chronic fatigue
- Reduced libido or sexual performance issues
- Mood swings, irritability, or depression
- Loss of muscle mass and increased body fat
- Difficulty concentrating or memory issues (brain fog)
- Sleep disturbances or insomnia
- Decreased motivation or confidence
- Hot flashes or night sweats (less common, but possible)

Causes of Andropause
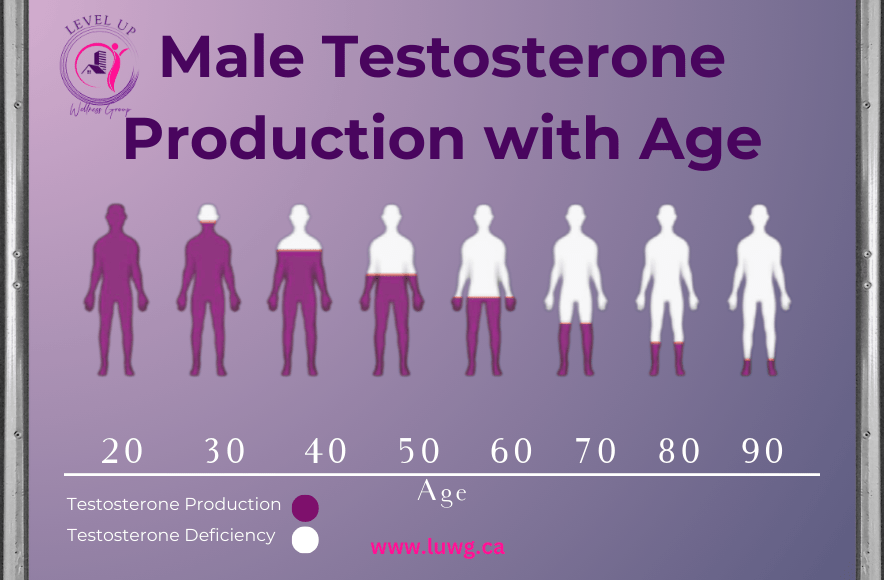
The primary cause of andropause is the gradual decline of testosterone, a hormone crucial for male reproductive and metabolic health. Testosterone levels begin to decrease around the age of 30, dropping by about 1% each year. For some men, the decline is more pronounced and leads to significant symptoms.
Contributing factors may include:
- Chronic stress or cortisol elevation
- Poor nutrition and lack of exercise
- Alcohol or drug use
- Obesity or insulin resistance
- Sleep apnea or chronic sleep deprivation
- Underlying health conditions (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease)
The Stages of Andropause
Andropause can unfold over time in several identifiable stages:
Stage 1: Subtle Decline
- Slight changes in mood, energy, and libido
- Often misattributed to stress or aging
Stage 2: Noticeable Symptoms
- Decline in physical strength, stamina, and sexual function
- Increased irritability or anxiety
Stage 3: Hormonal Imbalance
- Blood tests confirm low testosterone levels
- Other hormone levels may also be affected (e.g., DHEA, cortisol)
Stage 4: Seeking Help
- Symptoms affect quality of life and daily function
- Men seek medical advice, lifestyle changes, or hormone therapy
Stage 5: Stabilization and Management
- With appropriate treatment, many men see significant symptom relief
- Ongoing monitoring and lifestyle support are crucial
Icons from icons8.com
Diagnosing Andropause
If you suspect andropause, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests to measure total and free testosterone levels
- Thyroid and adrenal function tests
- Lipid profiles and blood sugar levels
- Mental health screening for anxiety or depression
Proper diagnosis ensures that symptoms are not due to other treatable medical issues.
Andropause vs. Low Testosterone (Low T)
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, andropause encompasses more than just low testosterone. It includes broader hormonal shifts and a wider range of emotional and cognitive symptoms. Low T is a component of andropause but can occur independently in younger men due to medical conditions or lifestyle factors.
Treatment and Management of Andropause
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Adopt a whole-food, nutrient-rich diet
- Engage in regular strength training and aerobic exercise
- Get quality sleep (7–9 hours per night)
- Manage stress through mindfulness, therapy, or hobbies
2. Supplements and Natural Supports
- Vitamin D, zinc, magnesium, and omega-3s can support hormone balance
- Adaptogens like ashwagandha or maca root may help boost libido and energy
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can be administered through injections, gels, or patches
- Requires regular monitoring to avoid side effects such as acne, fluid retention, or changes in blood pressure
- Not suitable for all men; consult about risks and benefits
4. Mental Health Support
- Andropause can bring emotional strain; individual counselling, relationship therapy, or support groups can be beneficial
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
At what age does andropause typically begin?
It can begin as early as the late 30s or early 40s, but symptoms often become noticeable between ages 45 and 65.
Is andropause the same for every man?
No. The rate of testosterone decline, symptom severity, and emotional impact vary significantly between individuals.
Can andropause be reversed?
While the natural decline in testosterone can’t be completely reversed, symptoms can be effectively managed with treatment.
How is testosterone replacement therapy monitored?
Doctors will monitor testosterone levels, red blood cell count, liver function, and PSA levels every few months to ensure safe treatment.
Can diet really impact hormone levels?
Absolutely. Diets high in refined sugars and processed foods can impair hormone production. A balanced diet with whole foods can improve energy, mood, and hormonal function.
Should I see a specialist?
Yes. A hormone health specialist can provide more targeted care than a general practitioner.
Is andropause linked to other health risks?
Yes. Unmanaged low testosterone levels are linked to higher risks of osteoporosis, cardiovascular issues, insulin resistance, and depression.
Final Thoughts
Andropause is a real, life-altering experience for many men. Understanding the signs and seeking help early can make a world of difference. You don’t have to suffer in silence or accept symptoms as a normal part of aging.
At Level Up Wellness Group (LUWG), we specialize in men’s hormone health, offering holistic, evidence-based care for andropause and related conditions. Our team is here to help you navigate hormonal changes and feel empowered in your health journey.