Testosterone is essential for male health, influencing everything from physical performance to emotional stability. However, many men experience a decline in testosterone levels, often without realizing it. Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, can significantly impact quality of life, making it essential to understand its signs, symptoms, and treatments.
In this article, we explore the critical role of testosterone, how to recognize its deficiency, and effective solutions to restore hormonal balance.
For additional insights on male hormonal health
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, produced mainly in the testicles, responsible for:
- Reproductive Health: Enhancing libido and sperm production.
- Physical Development: Promoting muscle mass, bone density, and body hair growth.
- Cognitive Function: Supporting mood regulation and focus.
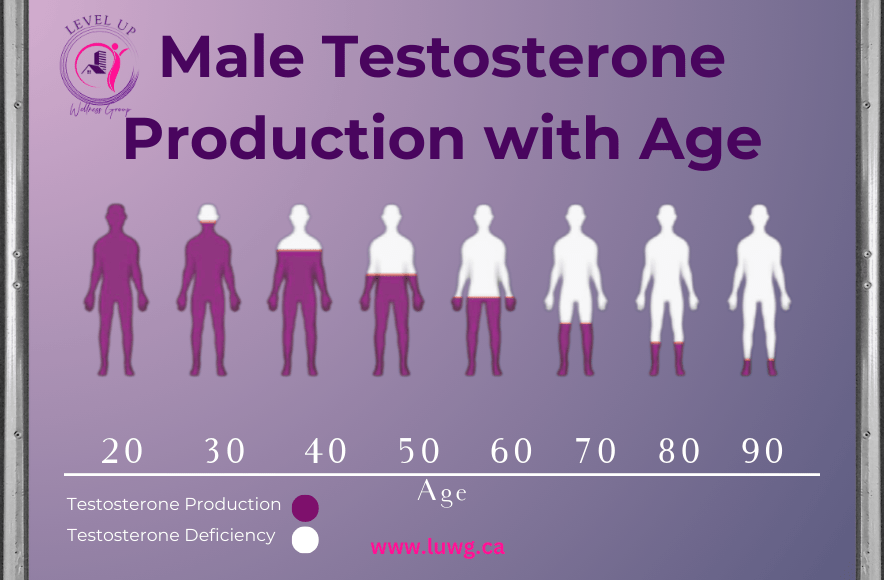
While testosterone levels peak during adolescence and early adulthood, they gradually decline with age—about 1% annually after 30. When levels drop too low, men may experience significant physical, emotional, and sexual health issues.
Explore more about overall health services at Level Up Wellness Group.
Common Causes of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone can stem from several factors, such as:
- Age: Natural aging reduces testosterone production.
- Medical Conditions: Obesity, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances can disrupt testosterone levels.
- Lifestyle Choices: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and chronic stress are common contributors.
- Injury or Surgery: Testicular trauma or surgeries affecting hormone regulation may result in low testosterone.
To learn about managing these risks, check out Male Hormone Health.
Physical Symptoms of Low Testosterone
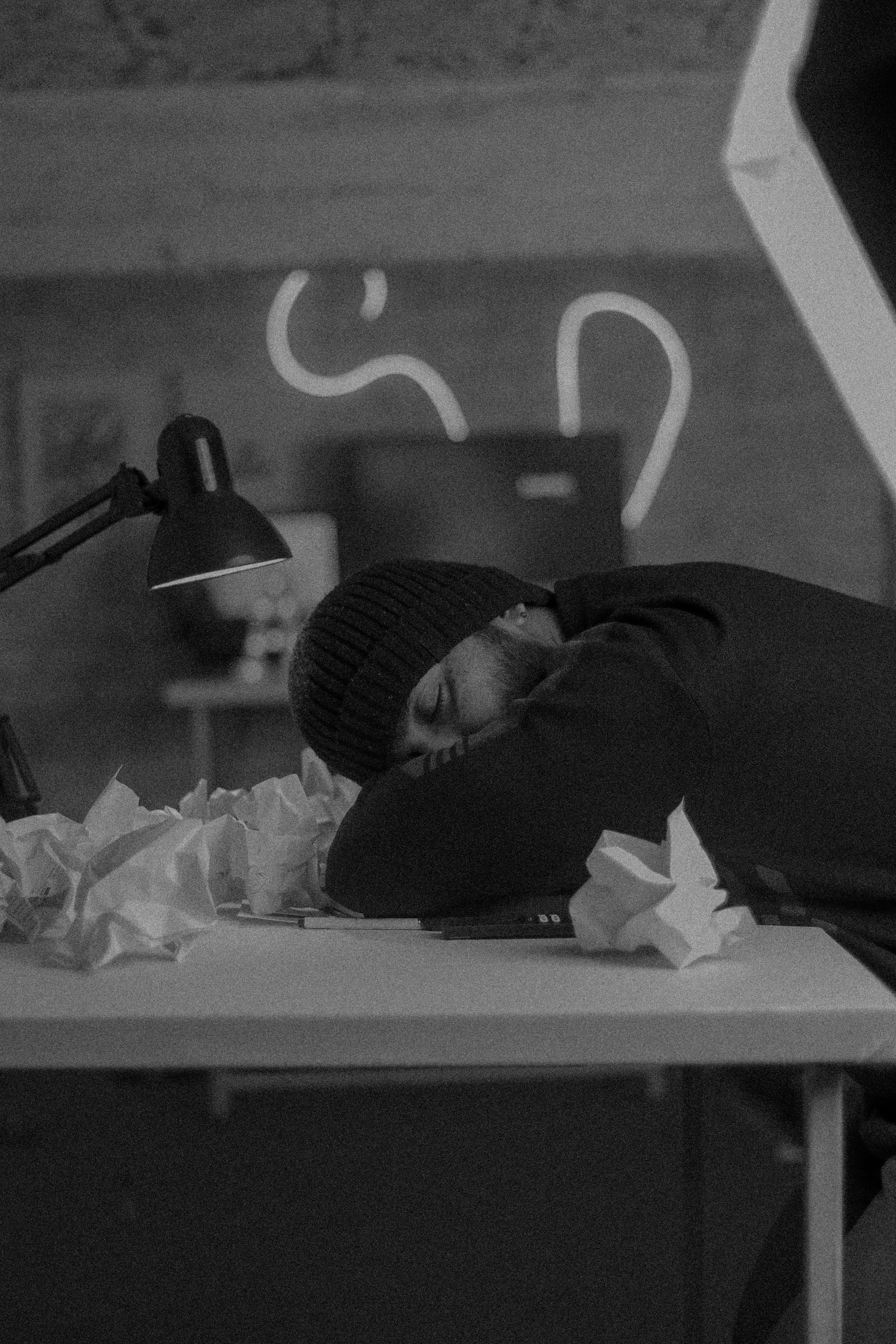

Low testosterone often presents through physical changes, including:
- Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest.
- Weight Gain: Particularly around the abdomen.
- Muscle Loss: Decreased muscle strength and mass.
- Hair Thinning: Loss of facial, body, or scalp hair.
- Weakened Bones: Increased susceptibility to fractures.
If these symptoms occur, it’s essential to consider a hormonal evaluation.
Emotional and Mental Symptoms
Beyond the physical effects, low testosterone can influence mental health:
- Depression: Persistent sadness and lack of interest in activities.
- Low Confidence: Decreased self-esteem and motivation.
- Irritability: Increased frustration over minor issues.
- Cognitive Challenges: Difficulty concentrating or remembering information.
These symptoms may disrupt relationships, work, and daily life.

Sexual Symptoms
Sexual health symptoms are often the most noticeable signs of low testosterone:
- Reduced Libido: A marked decrease in sexual interest.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Decreased Sperm Production: Lower fertility rates.
- Less Satisfying Orgasms: Reduced sexual pleasure.
If these issues persist, consult a healthcare provider. For professional guidance, visit Male Hormone Health.
How is Low Testosterone Diagnosed?
Diagnosing low testosterone involves:
- Blood Tests: Measuring total and free testosterone levels.
- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms and underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination: Checking for physical changes like reduced muscle mass or testicular abnormalities.
Doctors may also perform additional tests to identify other potential causes of the symptoms.
Long-Term Health Risks of Low Testosterone
Untreated low testosterone can lead to severe complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Osteoporosis: Weak bones prone to fractures.
- Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of obesity, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol.
- Cognitive Decline: Greater susceptibility to memory issues and dementia.
These risks emphasize the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Boost Testosterone
Medical Treatments for Low Testosterone
When lifestyle adjustments aren’t enough, medical treatments can help:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Administered via injections, gels, or patches to restore testosterone levels.
- Medications: Options like clomiphene citrate or hCG stimulate natural hormone production.
Consult a specialist for personalized recommendations. Find more information on professional health services at Level UpWellness Group.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
Natural approaches may complement other treatments:
- Herbs: Fenugreek and ashwagandha are believed to support testosterone production.
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- Vitamin D: A critical hormone precursor.
- Zinc and Magnesium: Essential for hormone synthesis.
- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporate testosterone-friendly foods like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens.
While promising, these remedies should be used under professional supervision.
When to See a Doctor:
Seek medical attention if you experience:
Persistent symptoms of low testosterone.
Significant changes in mood, energy, or sexual health.
No improvement with lifestyle changes alone.
Early intervention can prevent complications and improve overall well-being.
Myths and Misconceptions About Testosterone
Dispelling common myths can help men make informed decisions:
- “Low testosterone only affects older men.”
Reality: Younger men can also experience hormonal imbalances due to lifestyle or medical conditions. - “Testosterone therapy is dangerous.”
Reality: When monitored by healthcare professionals, it’s generally safe and effective. - “Natural supplements are sufficient for treatment.”
Reality: Severe deficiencies often require medical intervention.
Learn more about managing testosterone health at Male Hormone Health.
FAQs
What are the common signs of low testosterone?
Chronic fatigue, low libido, mood swings, and muscle loss are common indicators.
Can exercise boost testosterone naturally?
Yes, strength training and high-intensity workouts are effective ways to improve hormone levels.
What foods can help increase testosterone?
Foods rich in zinc, vitamin D, and healthy fats—such as eggs, nuts, and fatty fish—can help.
How is low testosterone diagnosed?
Through blood tests, medical history reviews, and physical examinations.
Is testosterone therapy safe?
Yes, under medical supervision, it is a safe and effective treatment for low testosterone.
At what age does testosterone naturally decline?
Testosterone typically starts to decline around age 30, decreasing about 1% annually.
Conclusion
Low testosterone can significantly impact a man’s quality of life, from physical symptoms like fatigue and muscle loss to emotional challenges and sexual health issues. Recognizing these signs and seeking timely treatment—whether through lifestyle changes, medical therapies, or natural remedies—can help men regain vitality and confidence.
For professional advice and treatment options contact us.